
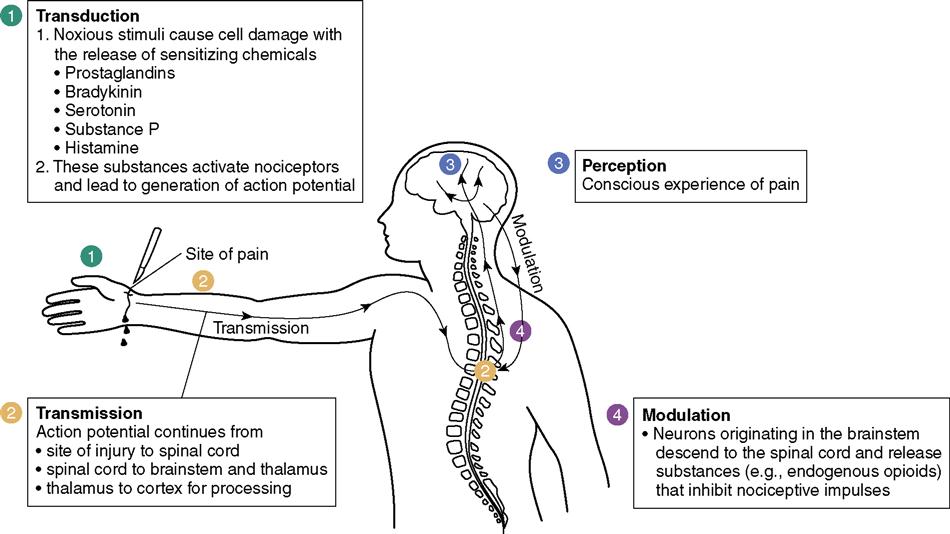
Absence of noticeable signs and symptoms of disease.There must be the presence of disease agent in the body.The Typhoid Mary is an example of a carrier.Epidemiologically, carriers are more infectious because they are not recognized and live as normal in community.A carrier is defined as ‘ an infected person or animal that harbors a specific infectious agent in the absence of the clinical disease and serve as a potential source of infection for others’.The host does not shed the infectious agent in latent infection.
#Transmit definition physiology skin#
Subclinical infection can be detected by lab test, isolation of micro-organisms, antibody assay, biochemical and skin sensitivity tests.They are important source of infection because they do not show any signs and symptoms of disease and shed infectious agent continuously.The subclinical cases are also called inapparent cases.The mild cases are more important source of infection as compared to severe cases.The clinical case may be mild or moderate, typical or atypical, severe or fatal.The cases maybe clinical, sub-clinical or latent.The cases are identified by clinical, biochemical and laboratory tests.A case is defined as ‘ a person in the population or study group detected as having the particular disease, health disorder or condition under investigation.’.Human himself is the important source or reservoir of infections.In tetanus, the reservoir and source are the same, which is the soil.In hookworm infection, the reservoir is a man, but the source of infection is the soil contaminated with infective larvae.Example: in typhoid fever the reservoir of infection is human but the source of infection may be faeces or urine of patients or contaminated food or water.Reservoirs is the natural habitat in which the microorganisms metabolizes and replicates.Reservoirs may be either animate or inanimate.Reservoirs are sites in which viable infectious agents remain alive and from which infection of individuals may occur.A source of infection is defined as the person, animal, objects or substance from which an infectious agent passes or is disseminated to the host.The medical model of infectious disease transmission consists of three interlinked chains. Diseases are transmitted from the source of infection to susceptible host.Dynamics of disease transmission: Reservoir, Mode of transmission and Susceptible host


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
